food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome in adults
Instead it can take hours before severe symptoms begin. Bryan N Fernandes Robert J Boyle Claudia Gore Angela Simpson Adnan Custovic.

I Talked To 30 Adults With Fpies This Is What I Found Fpies Roadmap
FPIES OFC methods vary globally and there is no universally agreed upon protocol.

. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults. From a diagnosis that did not exist to a condition in need of answers. High risk foods include milk soy rice oats and poultry.
Lessor reactions can cause extreme nausea and diarrhea. Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and usually occur 2-3 hours after eating a food. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES.
From a diagnosis that did not exist to a condition in need of answers. Bartnikas LM Nowak-Wegrzyn A Schultz F Phipatanakul W Bingemann TA. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy that manifests with projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and may be accompanied by. Food Protein-induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES For most people the term food allergy brings to mind symptoms like anaphylaxis hives or an itchy swollen mouth. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a nonIgE-mediated food allergic disorder that can manifest with symptoms of projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and may be accompanied by lethargy hypotonia hypotension hypothermia and metabolic derangements.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults. 1 In about 1520 of the reactions severe dehydration with hypotension and metabolic derangements. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES.
1 FPIES usually starts in infancy although onset at older ages is. There are a variety of foods that have been reported to trigger FPIES. Symptoms of FPIES for adults are usually the classic vomiting and diarrhea that occur 2-4 hours after a reaction.
Many allergists report that symptoms suggestive of FPIES are on occasion reported by adult patients and mainly refer to ingestion of seafood. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract. We report a case of a similar syndrome in an adult following ingestion of egg.
Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1265489-497 12 Jan 2021 Cited by. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract mainly in infants and young children. In its acute form FPIES presents with vomiting that usually begins 1 to 4 hours after trigger food ingestion can be 30 minutes to 6 or more hours.
Moderate risk foods that trigger FPIES include squash carrot white potato green beans apple. They can also have shaking low body temperature or fever. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
An acute form and a chronic form. Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food proteinFPIES presents in two different forms.
The evolution of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy that manifests with repetitive projectile vomiting within 14 hours following food ingestion frequently accompanied by pallor lethargy and may be followed by diarrhea within 68 hours. The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines.
Foods that cause FPIES. The evolution of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is typically diagnosed based on a characteristic clinical history.
1 2 This syndrome is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food. However an oral food challenge OFC may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis or evaluate for the development of tolerance. Adults with severe reactions can have vomiting to shock just like kids.
FPIES symptoms can be very serious and can include turning grey or blue dehydration and even going into shock. Food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome fpies adults Friday February 11 2022 Edit. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system. We remind clinicians to consider this diag-nosis which may present to emergency physicians and gastroenterologists long before an allergist is consulted. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare food allergy that affects the gastrointestinal GI tract.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy usually diagnosed in infancy. Most of the reactions were due to seafood mollusks crustaceans and fish and egg but other foods like peanut almond mushroom corn chicken and duck were also implicated. 0 articles PMID.
Also sweet potatoes peas banana egg and fish can be a trigger. 3 Diagnosis of FPIES is difficult. Unlike most food allergies symptoms of FPIES do not begin immediately after eating.
Annals of Allergy Asthma. Epub 2012 Jul 24. We report a case of a similar syndrome in an adult following ingestion of egg.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy usually diagnosed in infancy.
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Classification Scheme Of Fpies Fpies Food Protein Induced Download Scientific Diagram

Gastrointestinal Immunopathology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Other Non Immunoglobulin E Mediated Food Allergic Diseases Sciencedirect

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Foods Commonly Implicated In Food Protein Induced Enteropathy And Their Download Table

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
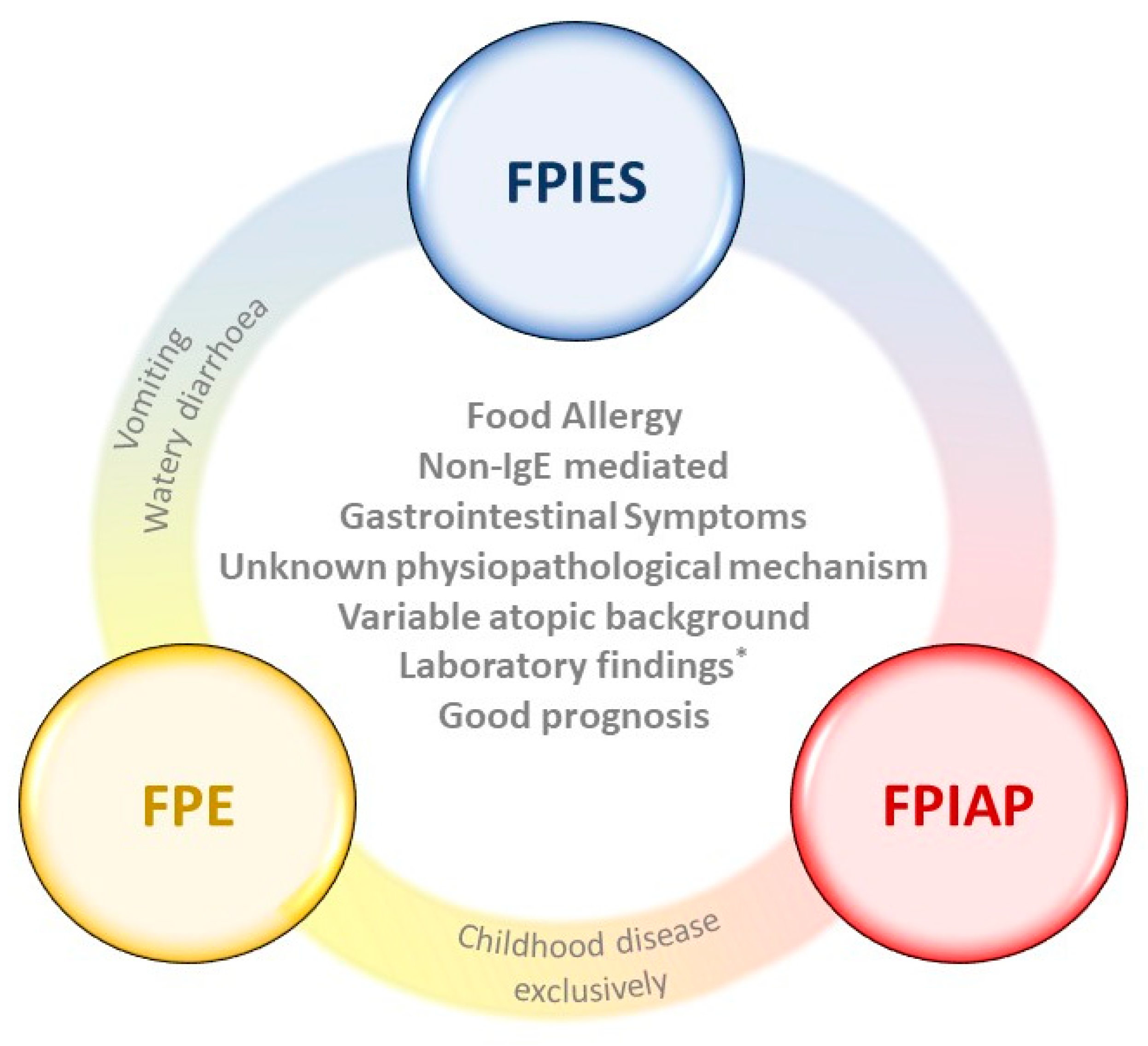
Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Dr Costa Private Children S Allergy Clinic

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
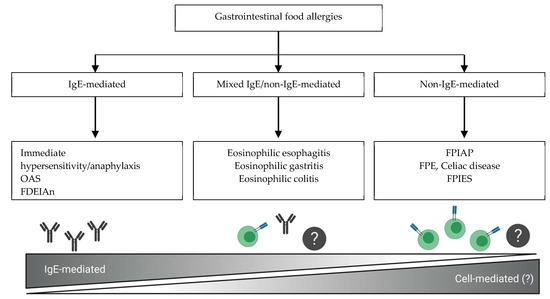
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice